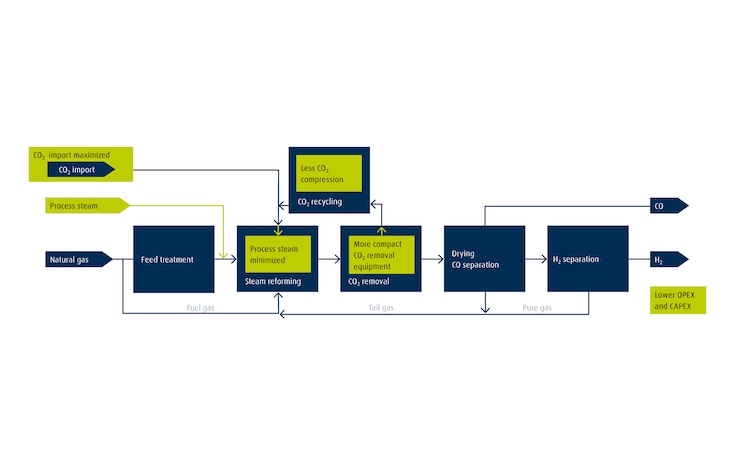
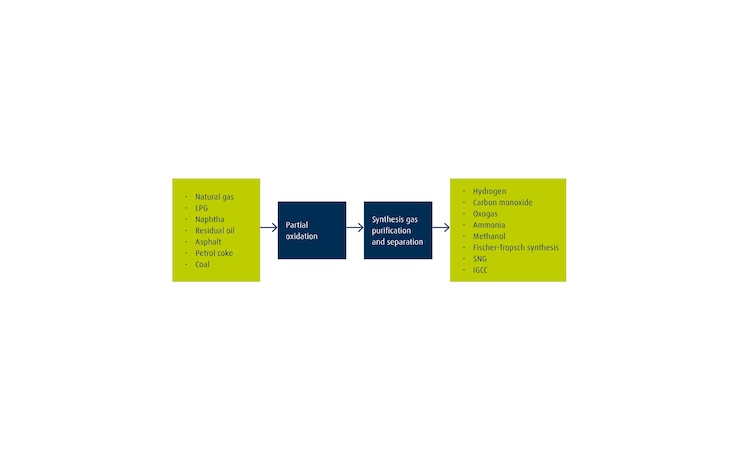
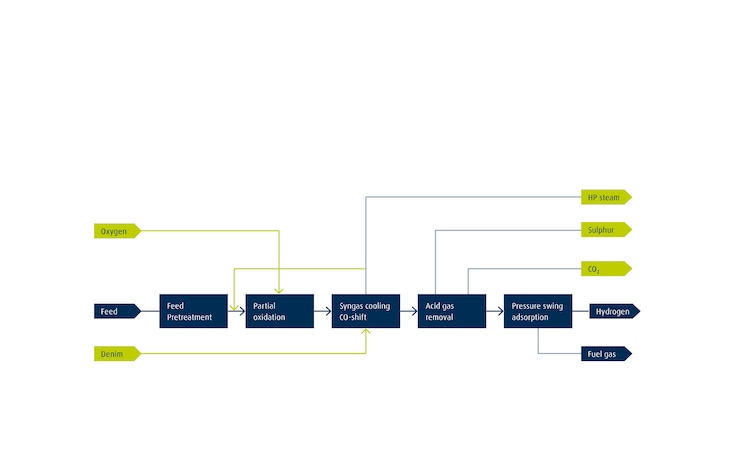
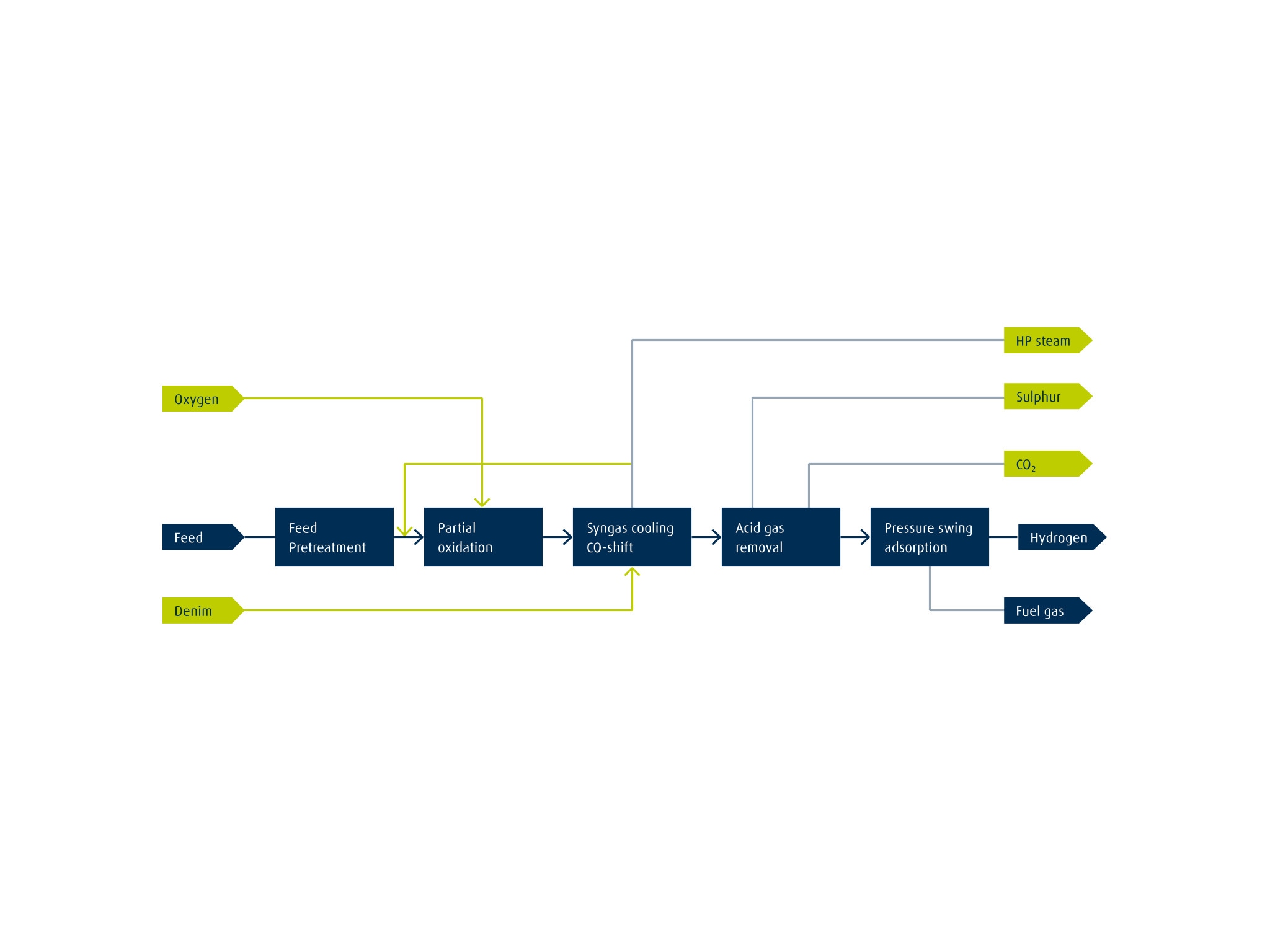
Electrolysis produces hydrogen (H2) by using electrical energy to split water into oxygen (O2) and H2. When renewable energy is used to split the water, the resulting H2 is green. The two main technologies currently deployed at scale are alkaline and proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis. Both electrolyzer technologies can deliver high-purity H2 on demand and on site.
Alkaline Electrolysis
Alkaline electrolysis is a very well-established technology that uses two electrodes separated by a porous diaphragm and a liquid alkaline solution as the electrolyte. The electrolyte solution allows hydroxide ions to be transported between the electrodes to form H2 and O2. It is not, however, consumed during the reaction. This technology is extremely efficient, reliable and cost-effective. We have extensive experience in this area, having installed over 80 alkaline electrolyzers globally.
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM)
PEM electrolysis uses pure water and a solid polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid solution. The electricity splits the water into H2 and O2. Hydrogen protons pass through the membrane, combining with electrons to form H2 gas on the cathode side.
PEM electrolyzers are well suited to volatile renewable energy sources thanks to their fast ramp-up/down capabilities and their wide dynamic operating range. No corrosive electrolyte is involved, and they operate at high current density, which speeds up the breakdown of the water molecule, ultimately favorably impacting the production price. Finally, a small footprint and compact system design is a benefit for many on-site industrial applications.
Learn more about electrolysis here